- Learn
- The B2B Enablement Hub
- How do I optimise my site for voice search?
How do I optimise my site for voice search?
Custom title applied. Post title: How do I optimise my site for voice search?By Daniel Falk

In recent years, the use of voice-activated devices has skyrocketed, and voice search has become a popular way for people to find information online. As a result, optimizing your website for voice search is now more important than ever.
Voice search offers a unique opportunity for businesses and website owners to reach a wider audience, and by following the right strategies, you can improve the visibility of your website and drive more traffic to your site. In this article, I will explore the importance of voice search optimisation and provide tips and best practices for optimizing your website for voice search.
Voice recognition paved the way for voice search
Voice recognition paved the way for smart assistants and voice search. Voice recognition has been developed by computer scientists since the Fifties. The first speech recognition system was called Audrey and was designed by Davis, Biddulph, and Balashek at the Bell Laboratories in 1952. It was a fully analogic system that could recognise strings of digits with pauses in the between. It had an accuracy of 97-99% of the system was adapted to the speaker.
Faster computers mean better voice understanding
Developments in voice recognition have largely been driven by Moore's Law, i.e. faster computers have contributed to better voice recognition systems. In addition to increased computer capacity, there have also been several significant leaps in development since the 1950s—for example, understanding how HMM models could be used to improve language comprehension.
Since 2010, Natural language processing (NLP) supported by AI, deep learning and big data have also played a significant role in how well these systems can understand natural language.
Voice search became big as the smart speaker market grew
Thanks to developments in this area, Google introduced voice search in 2011. First, Google made it possible to use voice to search Google.com via a Chrome browser. Then it was extended to voice commands for Android phones, and more languages were added over time. By 2017, it was possible to use Google Voice Search in over 120 languages.
The development and sales of smart speakers and other voice-enabled devices have exploded since 2016 when Google introduced its first smart speaker. Google was not the only company to develop this type of device. Amazon also introduced its Echo in late 2015, offering everything from music and lighting control to answers to direct questions.
Voice search stats
By 2020, there were estimated to be around 4 billion so-called voice assistants in various devices worldwide. By 2023, the number of such devices is expected to have increased to nearly 8.5 billion. This means that a large number of people will always have access to a voice assistant and the possibilities it offers.
A 2020 survey shows that over 40% of internet users in the US use voice search. Over 70% say they prefer voice search to keyboard search. Although it is now possible to do quite advanced things via voice search, such as shopping online, ordering tickets, booking appointments etc., the most commonly used functions are asking questions and doing simpler things, such as setting reminders, playing music or turning on lights at home.
According to this study, smartphones/tablets/computers and smart speakers are the most popular devices for voice search. Another area where voice search is growing and is also a very suitable application is in the car. Many new cars are equipped with software from Google or Apple which allows voice commands, voice searches etc. In the car, voice searches are likely to help you navigate and find shops, businesses, etc.
Looking for information about things in geographic proximity is big
According to this study on "Voice Search for Local Business, at least 58% of consumers in the US have used voice searches to find local businesses or experiences in the last 12 months. Most people use voice search to find information about companies they already know about.
The main differences between voice and text search
But are there differences in how people search by voice compared to written searches? Yes, there are two main differences:
- More words are used when people search with their voice because it's easier. Voice searches often contain more words than text-based searches. People are lazy by nature, and entering text into, for example, a mobile device is time-consuming.
- People tend to minimise the number of unnecessary filler words and instead use the main two to three words needed to get an answer to their query. Saying a sentence of 5-10 words is much faster than typing them. Therefore voice searches are longer.
Conversational questions are asked
You use natural speech when doing voice searches via your mobile or smart speaker because it is easier and more natural. The voice searches are simply of conversational type.
Google themselves say that at least 70% of these searches are of a conversational type, and in addition, there are more and longer follow-up queries.
How to conduct keyword research with a focus on voice search optimisation?
Since many voice searches contain a query, you must keep this in mind when conducting your keyword research. You can follow your usual process around keyword research. You can still use the same methods and tools, but when choosing the keywords you want to target, you should select more questions as keywords.
Search on Google to understand which questions are most common
A good way to find questions related to a topic is to do a Google search for the main keywords related to the topic. Google today often shows questions related to the search being made.
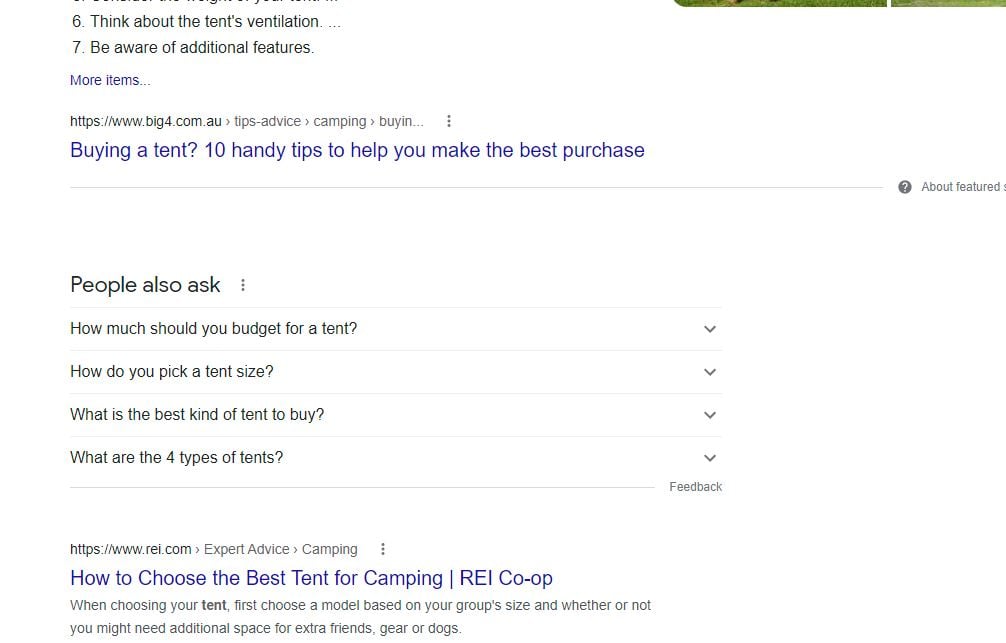
These are often frequently asked questions important to answer in the content you produce. Google probably shows these questions because many people asked them or looked for answers to them in the past.
Create a list of all the queries you find on Google search results
Imagine that you are going to write an article about buying a tent. Through research on Google, you can identify that the following questions are frequently asked:
"How much should I budget for the purchase of a tent?"
"How do I choose the right size for my tent?"
"What types of tents are there?"
"What is the best type of tent to buy?"
"Best places to buy a tent?"
Don't forget to look for related searches and buying guides on Google
In addition to these questions, you can also look at related searches that often appear at the bottom of Google's search results. Use and be inspired by the information displayed on Google. It's based on Google's knowledge that this interests searchers.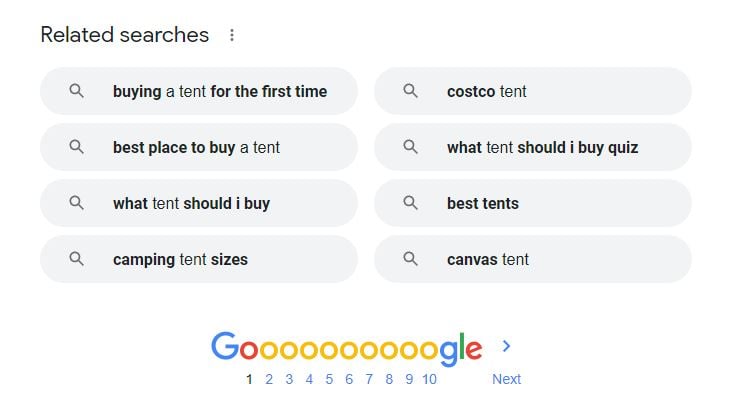
If you do searches related to shopping, as in this example, you may also see buying guides from Google. This section can show information that is valuable for finding questions and answers that are interesting to include to optimise your content for voice search.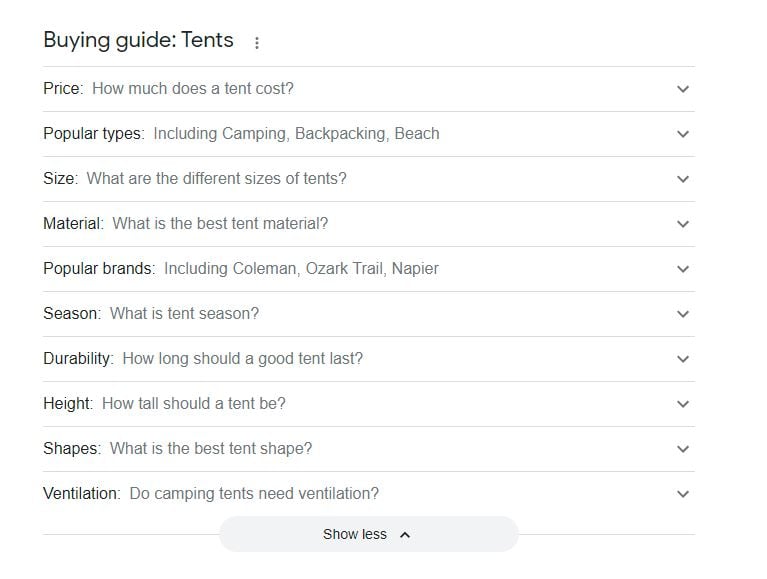
You can also use tools designed for keyword research. These tools allow you to filter specifically on queries within a topic. If you have access to an SEO tool such as SEMrush, Ahref, Moz or similar, you can, of course also use these to find keywords/questions related to the topic. I am a frequent user of SEMrush, and in their module "Keyword Magic Tool", there is the possibility to filter suggested keywords on "general keywords" and "questions". Since this tool gives me direct access to search volume, difficulty, CPC cost and intent, it is easy to select the most interesting keywords.
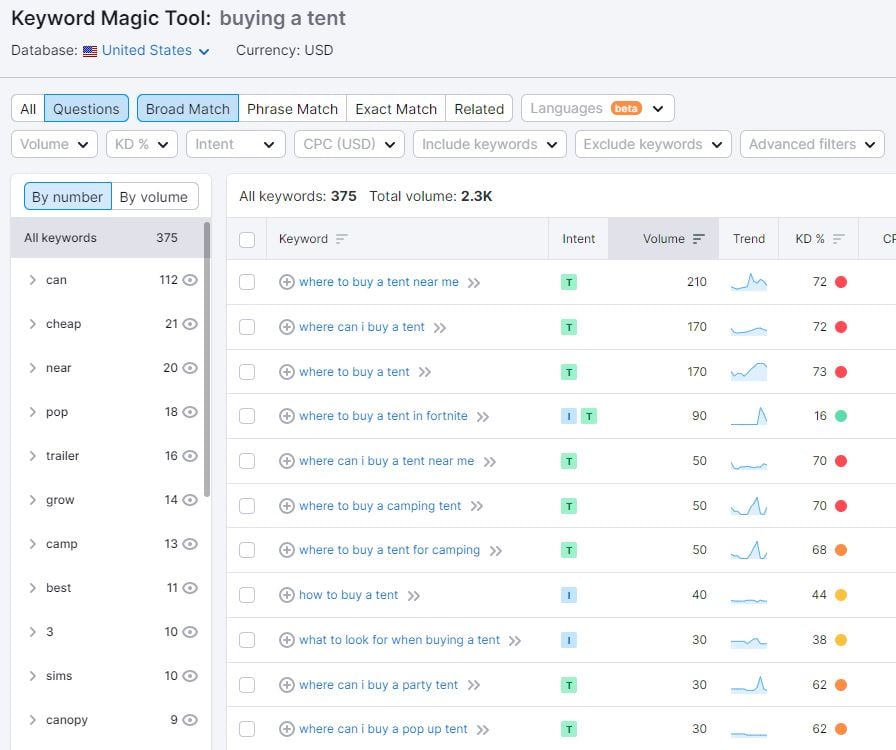
Some other tools focus specifically on queries. One that I have started to use a lot lately is AnswerThePublic. The advantage of this tool is that it focuses specifically on questions asked online. When I enter my topic about buying a tent in this tool, I get interesting and structured information about the different questions about purchasing a tent. The image below shows one type of illustrated data that can be obtained from this tool.
In this case, I did an initial search for "tent" and the tool then returned a range of queries related to this keyword. The screenshot shows only queries related to "are tent" but you also get lists based on "can tent", "how tent", "what tent" etc.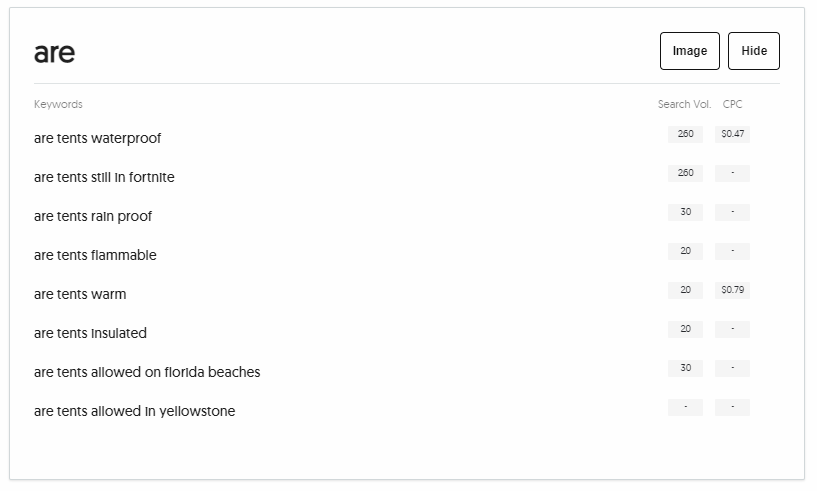
From AnswerThePublic you can also get the results presented in a circular format where all questions are visualised together with search volumes (if you are using the PRO version):
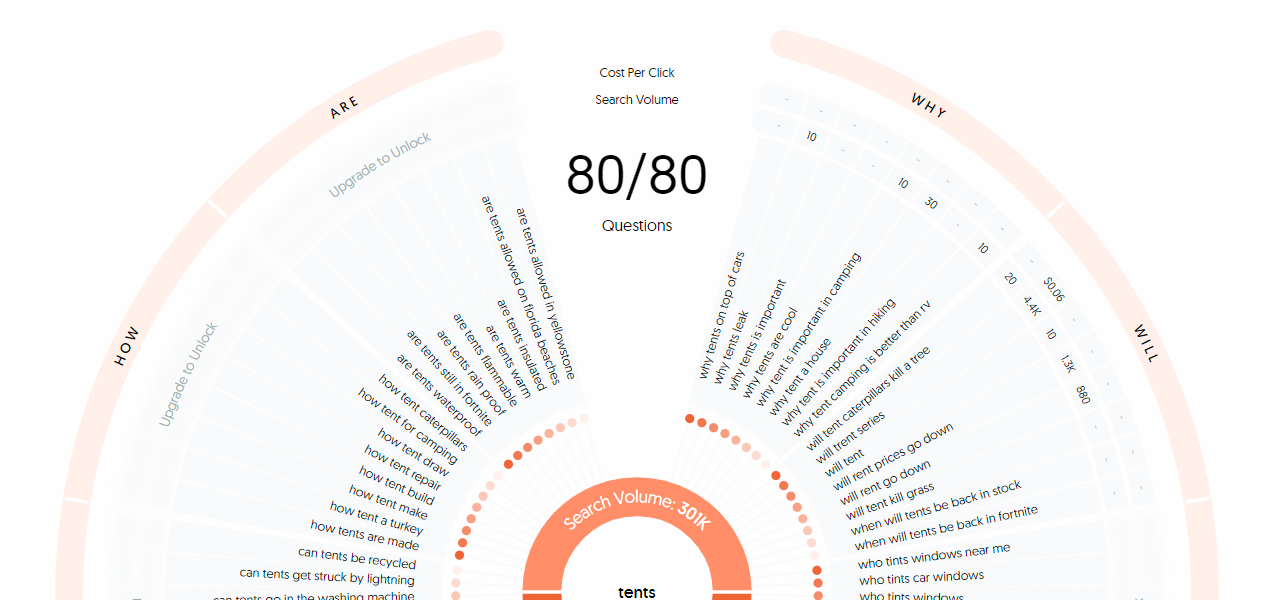
Always do a manual review of the search phrases
As you can see in one of the the screenshots above, some irrelevant keywords such as "where to buy a tent in Fortnite" are included. So, as always in keyword research, you therefore need to make a manual assessment of whether the keywords are relevant to include in your content or not.
Another tool that does much the same as AnswerThePublic but where the presentation of the results is a bit more basic is KeywordSea. In this tool you enter your main keywords, then the tool fills in with questions related to these keywords structured by "what", "when", "where", "who". Collect too many questions rather than too few. You will benefit from them both in content production and follow-up
Collect all the queries you find that are related to the topic in your keyword research document. Then enrich the list with information such as monthly search volume, difficulty, intent, etc. if this was not included in exported lists from the tools you use.
Structure your article based on the keyword research
By grouping the keywords and questions from your research, you can create a structure or outline for the article. From the groups, you will understand which topics you need to cover and which groups and questions you need to answer to optimise for voice search.
The wire-frame below shows a simple example on how the structure of the article can be built based on your keyword research. The questions and topics you've identified during the keyword research phase will help you understand what the article should contain for the visitor to get answers to their questions.

How to formulate questions to increase the likelihood that your page will be selected as an answer for a voice search?
When building your content page, it is important to structure it so that questions and answers are clearly linked. It's is important to give a short and concise answer immediately below the question. This increases the likelihood that Google will include them as answers in voice searches.
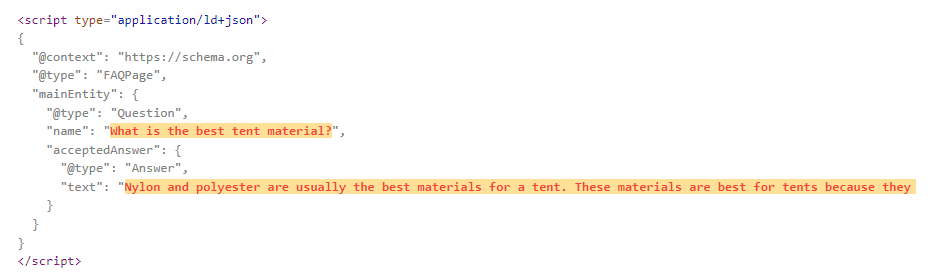
In our example of questions about tents, one of the questions and the answer could look like this:
| Question: What is the best tent material? Answer: Nylon and polyester are usually the best materials for a tent. These materials are best for tents because they are cheap, weigh little and dry quickly. |
Implement schema markup for FAQs
By implementing FAQ schema markup you provide structured information to the search engines. This information is easier for them to interpret as the question and answer are clearly defined. Implementing this is not something that will individually make you rank better or appear more often as an answer in voice search. The authority of the site, the quality of the content and the structure are more important. But when the rest is in place, schema markup can contribute to better results.
Read more in Google's documentation on FAQ schema markup. I also recommend this tool which makes it easy to generate the required code. From this tool I created the following example code for the question "What's the best tent material":
Use your long list of keywords to track ranking progress
Be sure to keep the list as you will need it for monitoring how well your new content is performing. By inputting the keywords into the tool you (may) use to check search engine rankings, you can track your visibility on these keywords and queries over time.
You can always get data via Google Search Console, but that's assuming you've started ranking on the keywords. By checking them via a dedicated ranking monitoring tool, you can get a more accurate view of trends and you can also identify which groups of words are doing well and which are doing poorly. This way you can optimise your article if you are not achieving the desired results for a group of keywords/queries.
Summary of how to research and optimize your content for voice search
- Use natural language: When creating content, use natural language that sounds like the way people speak. Avoid using technical jargon and abbreviations, as they are often difficult for voice assistants to understand.
- Use short and concise content: Voice search results are usually shorter than text-based search results, so it's important to keep your content short, concise, and to the point.
- Optimize for long-tail questions: Long-tail questions, which are longer and more specific phrases, are more likely to be used in voice searches. Make sure to include long-tail questions in your content and use them in a natural and conversational manner.
- Create content for featured snippets: Featured snippets are short pieces of information that appear at the top of search engine results pages. Create content that answers common questions related to your business or industry in a clear and concise manner to increase your chances of appearing in a featured snippet.
- Use schema markup: Schema markup is a way of marking up your website's content to provide additional information to search engines. Use schema markup to indicate the type of content on your website and help search engines understand the context of your content.
If you require further guidance on optimising your website, please feel free to book a free meeting.

Keep updated on thoughts, facts and knowledge!
Related
-
By Daniel FalkSEO Outlook – July 2025
-
By Daniel FalkSEO Outlook – May 2025
-
By Mark HooleyGoogle updates: Vital information and strategies to boost your content
-
By Qarin LövgrenWriting for online #3: How to get people to click your links offsite
-
By Daniel FalkHow to create an effective SEO team structure for your business
-
By Fabian ZetterbergWhat to focus on when deciding keywords – and 3 research tools to use!